How It Works
Traditional approaches to disinfecting and sanitizing may not be able to keep up with the rising infectious disease crisis we are currently facing with Covid-19. Traditional methods are often ineffective, expensive and lack the tools or technology to ensure the job is done effectively or timely. This can result in unsafe, potentially contaminated environments that are breeding grounds for the ongoing spread of disease.
The Electrostatic Advantage
We’ve invested in the latest, most cutting-edge technology available in the industry combining electrostatic delivery with more conventional methods like fogging and misting. This allows us to provide 360˚ coverage around curved and hard to reach surfaces.
Our technology provides an electrostatic charge to each individual droplet, creating a magnetic field that draws the disinfectant to any surface within 6 feet.
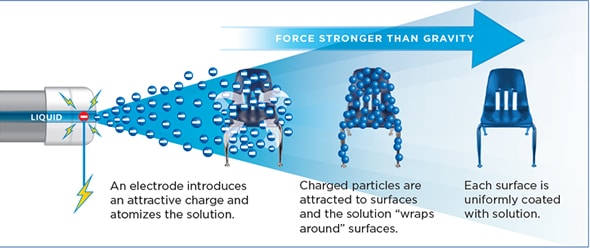
The droplets pass an electrode inside our equipment, creating a magnetically charged spray that seeks our and wraps around all touch points and grounded room surfaces.
With an attraction coefficient 15 times greater than gravity, the electrostatic force field is so powerful, the plume reverses direction to coat hidden and hard to reach surfaces that can be missed by conventional spraying or misting equipment.
KILL LIST
Our disinfectant is on the EPA list N and meets the criteria for use against SARS-COV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. It meets the emerging pathogen requirement for viruses showing efficacy against envelope and non-envelope viruses, both small and large when used in accordance with the directions for use against Norovirus on hard, porus/non-porous surfaces.
It has been scientifically proven to kill 99.999% of viruses, odor-causing bacteria, mold, allergens and odors including those listed below.
-
Salmonella enterica
-
Clostridium dicile
-
Staphylococcus eureus
-
Influenza virus H1N1
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
-
Respiratory syncytial virus
-
Klebsiella pneumoniae
-
Canine Parvovirus
-
Staphylococcus epidermidis
-
Newcastle Disease Virus
-
Escherichia coli 0157:H7
-
Pseudorabies
-
Staphylococcus aureus – Canine Distemper Virus
-
MRSA & GRSA Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1
-
Carbapenan resistant Klebsiella
-
Feline Calicivirus
-
Pneumoniae Norovirus
-
Acinetobacter baumannii
-
Enterococcus faecalis Vancomycin
-
Poliovirus type 1 Resistant
-
Herpes simplex virus type 1
-
Trichophyton mentagrophytes
-
Hepatitis A virus
-
Hepatitis B virus
-
Mycobacterium bovis (TB)
